1. Banks and business
Most businesses need to borrow money to finance (=pay for) inverstments.
The money they borrow from the bank is called a loan, and this loan they have to pay interest.
e.g. if you borrow $1,000 and the interest rate is 10%, then you have to pay back $1,000, plus $100 in interest.
2. Businesses and profit:
One of the main aims/objectives (n-mục đích, mục tiêu) (= the things that you hope to do/achieve) of a company is to make a profit (= earn/ receive more money than it spends). if a company does not make a profit (n- lợi nhuận) or a loss, it breaks even.
Most companies are happy if they can break even in their first year of business.
Companies receive money from selling their products - this money is called the turnover (n- doanh thu, doanh so).
The money that they spend is called the expenditure (n- phi tổn, sự tiêu dung).
They spend money on these things: raw materials (n-vật liệu thô) (= materials in their natural state used to make S.T else, e.g. coal and oil are important raw materials used to make plastics); labour (= employees); overheads (= necessary costs for a company, e.g. rent for building, electricity, telephone)
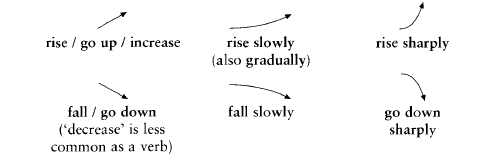
3. Rise and fall
Business people often need to talk about the movement of sales, prices, interest rates, profit and loss, etc. Here are some of the words used to describe these trends (n- phương hướng, xu hướng) (= movements):
Notes: rise, increase, and fall are also used as nouns: a slow rise in interest rates, a steady increase (adj- vững, đều đều) in sales, a sharp fall in profits, a dramatic (=sharp) rise in inflation (n- lạm phát). We can also use be up/down; prices are up by 10%; profits are down by $2m.
4. Businesses and the economy:
In order to grow/expand (= get bigger) and thrive/prosper (v- phát đạt, thịnh vượng) (= do well/ be successful), many companies want or need the following:
_ low inflation, so prices do not go up.
_ low interest rates, so the company can borrow money without paying a lot of interest economic and political stability (= things remain steady (adj- vững, chắc) and stable and there are not sudden (adj) changes in the economic and political situation).
_ a healthy/strong economy (= in good condition), and not an economy in recession (n- tình trạng suy thoái (= in a period of reduced and slow business activity)
_ tax cuts (= tax reductions/lower taxes), so they can keep more of their profit. This often depends on government expenditure, e.g. The government will not be able to reduce taxes if public expenditure continues to rise.
Others:
The continuous increase in the price of things.
Fortunately the company is doing well now.
And it's growing very quickly.
This is one of their main objectives.
Profit have risen considerably.
What is the current inflation rate?
What is the state of the economy at the moment?
Do you think business are optimistic about the future?
Has the government reduced company taxes or personal taxes in the last twelve months?
Has public expenditure risen of fallen int the last twelve months?
Describe the graph as following:
In 1992 sales rose.
In the following year they fell slightly.
In 1995 there was a sharp fall in sales.
In 1996 business improved and there was a steady rise.
And in 1997 sales rose sharply
In the five-year period sales rose by 40,000.


0 comments
Post a Comment