1. Cash, cheques and cards
_ I was broke/skint at the end of last month. (had no money left; broke = informal; skint = very informal)
_ I'm rolling in it this month; I got a cheques for $3,000 for some work I did. (informal: have a lot of money)
_ It's diffocult to make ends meet sometimes with three children and only one parent working. (to survive financially)
_ Things are a bit tight at the moment. (informal: my finances are not good)
_ I was strapped for cash and had to borrow money from my parents. (informal: needed cash and had very little)
_ She gave me a cheque for what she owed me but it bounced. (the bank refused to pay it)
_ Who shall I make this cheque out to? (What name shall I put on it?)
_ Shall we put/stick this meal on my credit card? Then we can forget it. (informal)
_ Could you charge it to my credit card please? (formal)
_ The APR for this credit card is 23%, that's two per cent lower than my other card. (annual percentage rate of interest)
_ My card expires 05/04. (is not valid after)
_ Credit card fraud has increased in recent years. (illegal use of someone's card or account)
2. Saving, pensions, etc
The words in bold in these newsclips refer to longer-term aspect of personal finances.
_ Victims (n- nạn nhân) of last year's rail crash will receive lump sum (1) compensation (n- sự bồi thường) payments following a High Court decision today.
_ A golden handshake (2) of one milion pounds was paid to the boss of one of Britain's biggest companies today.
_ Mr Carslow had taken out an endowment (3) ten years earlier to pay for his son's education.
_ The thieves stole Mr and Mrs Freal's life-saving (4), which they kept under their bed in a metal box.
_ People will well-managed share portfolios (5) have done better than individuals who buy stocks and share privately.
(1) single, large payment
(2) large payment to someone on leaving a job
(3) combined insurance and savings plan that pays out after a fixed period.
(4) money saved over many years
(5) combination of stocks and shares of different kinds
Exercise:
_ This is a credit card. If you want one that you have to pay off each month, then you should get yourself a charge card.
_ She never used her card on 4th September. But someone did and bought hundreds of pounds of goods. It was a case of credit card fraud (n- gian lận)
_ I haven't got enough cash to pay for this meal, but they take credit cards; shall I just put/stick it on my credit card?
_ You'll take a cheque, will you? Good, Who should I make it out to?
_ He wrote me a cheque, but he had no money in his account so it bounced (v- đánh lừa).
_ I'm sorry, I can't lend you anything at all. I'm absolutely broke/skint.
_ I couldn't really afford it as I was a bit strapped for cash.
_ I have to be very careful how I spend my money; right now things are a bit tight.
_ The amount you pay each month or year for an insurance policy. (premium n- phi bao hiem)
_ A person who lends money at extremely high interest rates to people in financial difficulty. (loan shark)
_ Money you borrow to buy a house or flat. (mortgage)
_ Money you have to pay up to a certain level if you make an insurance claim. (excess)
_ Insurance you pay against illness. (health cover)
_ A scheme to provide you with an income when you retire. (pension plan)
1. International aid, debt and development
In a public question and answer session on the Internet in 1999, Clare Short, the Minister responsible for Britain's international development policies and activities, gave this answer to question from someone in Haraze, Zimbabwe.
Question: Are the UK and Europe tired of trying to encourage real and lasting deveplopment projects in Africa?
Answer:
_ It may surprise you to learn that there are many encouraging signs in Africa. Over the last three years, 31 Afrucan countries achieved economic growth of more than 3% per year.
_ Foreign direct investment, although still too small, has been rising. Africa's share in world trade has shown signs of recovering from its long decline. Some countries, such as Maxambique ..., have done much better than this.
_ But some 250 million people in Africa still live in deep poverty and we must do better. With other development agencies we are committed to supporting those African government which are following policies to reduce poverty and improve access to better health, education and clean water.
abject poverty is also a typical collocation
development grants are often given to poor regions. (money to help economic development)
sustainable development is the most important goal for most countries (development that does not destroy the economy/ the environment, etc)
2. Trade and cooperation
_ Free trade agreements often cause disputes between countries, especially when one country thinks the other is engaged in restrictive practice (1).
_ Occasionally, trade wars erupt, and sanctions (2) or embargoes (3) are imposed on countries, and may not be lifted for long periods.
_ On the other hand European countries closely related economically and enjoying good relations have entered into monetary union and have a single currency.
(1) the placing of unfair restrications, e.g. limiting imports.
(2) restrictions on what a country may import/export.
(3) total prohibition on importing/exporting certain goods.
3. Economic difficuties and negative practices
_ If an economy is badly affected by war, we may refer to it as a war-torn economy.
_ Econmies in a bad state are often referred to as ailing economies.
_ Devaluation/revaluation of the currency may be necessary. (reduction/increase in value against other currencies)
_ Economies may go into recession and not come out of/ emerge from recession for several years. A country may suffer from a slump in prices for its goods.
_ Fiscal measures may be used to boost the economy when it is in recession.
_ Development is important, but it should be sustainable development, not the kind that destroys the environment and social structure.
_ The government is following a policy of giving aid only where it is used to reduce poverty.
_ There have been some encouraging signs that development aid is working in many countries.
_ Millions of people still live in deep poverty.
_ The economy has recovered from its decline and is now doing well.
_ The struggle to achieve economic growth in developing countries is a constant one.
_ It is importance to encourage lasting development projects, not just short-term ones
_ The goal should be to improve access to better health and education for the poor.
_ Over a period of five years, the country incurred (got) huge debts which it could not repay (pay back).
_ Debtor countries (countries in debt) are completely at the mercy of the rich nations.
_ The burden of debt (The weight of debt) is so great in some countries that their economies are collapsing.
_ Rcher countries could do a lot to ease/ alleviate (make) the debt of poor countries and indeed, in some cases, could cancel (or write off) (forget) the debt altogether.
1. Here are some important words for talking about business agreements.
to put in/submit a tender: to supply a written offer to do a job for an agreed price.
to win a tender: to be given a job, after submitting a tender
to meet/miss a deadline: to supply/fail to supply something by the agreed time.
a penalty clause: part of a contract specifying what will happen if an agreement is broken.
an outstanding account: an account that has not yet been paid.
to default on a payment: to fail to pay something that had been agreed.
to acknowledge receipt: to inform the sender when something is received.
to ship an order: to send out goods that have been ordered - nothing to do with boats; what is sent is the shipment.
to expire: to end - of S.T that was agreed for a fixed period; the noun is expiry.
2. Reading humorous books about work can be a fun way of lerning new words on the topic.
Some rules of management (from a Handbook for Manager)
_ The problem is not lack of resources, it's a lack of meetings.
_ If you're talking, you're communicating (1).
_ Low morale (2) is caused by character flaws (3) in your employees.
_ If 10 people can complete a project in 10 days, then 1 person can complete the project in 1 day.
_ Teamwork (4) is when other people do your work for you.
(1) this verb suggests that listeners understand what the speaker is trying to convey (v- chuyển, truyền đạt).
(2) amount of confidence felt by a person or group.
(3) weaknesses
(4) working together for a common purpose.
3. Here are somethings that people have said about business:
_ We demand that big business give the people a square deal; in return we must insist that when any one engaged in big business honestly endeavors to do right, he shall himself be given a square deal. (Theodore Roosevelt)
_ It is difficult but not impossible to conduct strictly honest business. What is true is that honesty is incompatible with the amassing of a large fortune. (Mahatma Gandhi)
_ The growth of a large business is merely the survival of the fittest [...] The American Beauty rose can be produced in the splendour and fragrance which bring cheer to its beholder only by sacrificing the early buds which grow up around it. (John D. Rockefeller)
_ The salary of the chief executive of the large corporation is not a market award for achivement. It is frequently in the nature of a warm personal gesture by the individual to himself. (J.K. Galbraith)
_ Accountants are the witch-doctors of the modern world and willing to turn their hands to any kind of magic. (Lord Justice Harman)
_ British mangement doesn't seem to understand the importance of the human factor. (Charles, Price of Wales).
_ Do you have many outstanding accounts (accounts which have yet to be paid)
_ When does your contract expire? (Until what date is your contract valid?)
_ Please acknowledge receipt of our payment. (Please let us know when you receive our payment)
_ It is very important that you meet the deadline. (It is very important that you complete your work by the agreed time.)
_ We would like to invite companies to submit tenders for the job. (We would like to invite companies to send us proposals as to know they would do the job and what they would charge for it)
_ It is company policy to take legal action against customers who default on payment. (againt customers who fail to pay their accounts)
_ Joana is working on a very interesting project at the moment.
_ Unfortunately, there's a flaw (n- thiếu sót, sai lầm) in your reasoning (lý lẽ của bạn)
_ What used to be called Personel is now called Human Resources
_ The new manager is doing his best to raise morale (n- tinh thần, nhuệ khí) in the office.
_ Sadly our new product has met with a total lack of consumer interest.
_ We are extremely sorry to lose Matt as an employee.
_ Top businessmen often award themselves bonuses regardless of their performance.
_ It is impossible to be both rich and honest (chân thành).
_ Manager don't pay enough attention to the people who work for them.
_ Large businesses succeed by destroying small businesses.
_ Companies must treat customers fairly; then government will treat companies fairly too.
_ Jack is now the chief executive of a large company.
_ He managed to amass (v- tích lũy, cóp nhặt) a fortune by designing some computer software sold all over the world.
_ He's a talented man, prepared to turn his hand to any job that needs doing.
_ He is good to his employees, always them a square deal because he knows how important the human factor is if you want to conduct business successfully.
_ Last year he won an award for achivement (n- thành tích). In a remarkable personal gesture (n- điệu bộ, cử chỉ), he gave his prize money away to his employees.
1. Modern business techiques
_ When John left school he was desperate (adj- liều mạng; ko còn hy vọng) for a job so he took the first one he was offered in telesales (1). He thought telemarketing (2) sounded quite glamorous (adj- quyến rũ) but soon found that most of the people he phoned hated cold-calling (3) and put the phone down when he tried the hard sell (4).
_ When he realised that the company made most of its money through the rather dubious techniques of inertia (n- trì trệ) selling (5) and confusion (n- lộn xộn) marketing (4), he decided to leave and train as a hairdresser instead.
(1) selling or marketing goods and services by phone
(2) see note (1)
(3) phoning people who have not requested a call in order to try to sell them something.
(4) attempt to sell S.T by being very forceful.
(5) when a company behaves as if you agreed to buy S.T because you did not actually refuse it.
(6) selling products and services in a package, in a way that makes it very difficult to work out which company is cheapest.
2. Buying and selling
_ Supermarkets sometimes sell an iterm very cheaply just so that they attreact a lot of people into the shop where they will also buy more profitable items - the item being sold very cheaply is called a loss leader.
_ If a company finds a niche market (thị trường thích hợp), it find a specialised, small group of customers with particular interests that that company can meet.
_ People sometimes make a purchasing decision based on brand loyalty (n- lòng trung thành). (confidence in that particular make and a tendency (n- xu huong) always to choose it)
_ If you shop around, you try different companies or shops to see which offers best value.
_ If you buy something on approval, you have the right to return it if it is not satisfactory (adj- thỏa đáng, vừa ý).
_ If you have first refusal (n) on something, the seller promises that you will be asked if you would like to buy it first, and only if you do not want it will it be offered for sale to others.
_ If an item is said to come/go under the hammer, it is sold at an auction (n- cuộc đấu giá).
3. A business career:
_ Sally started her own catering business and this turned out to be very lucrative (1). However, she got increasingly irriated by all the red tape (2) involved in business and when a larger company suggested merging (3), she was interested.
_ The two companies did not agree immediately on all the details of the takeover but they managed to reach a compromise (n- sự thỏa hiệp, giàn xếp) (4) and hammer out a deal (5) without too much delay.
_ In some ways Sally was sad that her company had been swallowed up (6) but she is now quite glad to be free of the hassles (điều rắc rối, phức tạp) of entrepreneurship (7). She has used the money raised by the sale of her capital (n- vốn) assets (8) to buy a large house in the south of France.
(1) producing a lot of money
(2) bureaucracy (negative)
(3) joining together to form one new company
(4) come to an agreement in which both sides have to give in a little bit on what they would have otherwise liked.
(5) talk seriously and in detail until a business agreement is made.
(6) taken over by a larger company (slightly negative)
(7) involvement (bao hàm, bao gồm) in business and taking financial risks.
(8) buildings and machines owned by a company
Exercise:
_ A unique painting will come under the hammer in London tomorrow.
_ It's a sensible idea to shop around a bit before buying a computer.
_ Jeremy has promised me that, if he ever decides to sell his motorbike, I can have first refusal on it.
_ I don't mind trying a hard sell on a person who has already experssed an interest in our products, but I have cold-calling.
_ I wasn't sure whether the desk would fit into my office so I bought it on approval.
_ If you want to make a bid for something in an auction you first have to catch the autioneer's eye.
_ If you work in telesales you spend most of your day on the phone.
_ They produce special clothes for people who like to do yoga and have really captured this niche market.
_ As their business interests were really very similar, it did not take them very long to come to an agreement. (hammer out a deal)
_ If you want to go into the impoxt and export business, you had better be prepared for a lot of bureaucracy (n- công chức, sự quan liêu). (red tape)
_ At the moment they are discussing the possibility of their companies becoming one. (meriging)
_ Sportswear is very profitable business to be in at the moment. (lucrative adj- sinh loi)
_Only a few people have a real talent for the risk-taking of opening a new business. (entrepreneurship nha doanh nghiep)
_ A number of small companies have been taken over by that large multi-national in the last six months (swllowed up)
1. Banks and business
Most businesses need to borrow money to finance (=pay for) inverstments.
The money they borrow from the bank is called a loan, and this loan they have to pay interest.
e.g. if you borrow $1,000 and the interest rate is 10%, then you have to pay back $1,000, plus $100 in interest.
2. Businesses and profit:
One of the main aims/objectives (n-mục đích, mục tiêu) (= the things that you hope to do/achieve) of a company is to make a profit (= earn/ receive more money than it spends). if a company does not make a profit (n- lợi nhuận) or a loss, it breaks even.
Most companies are happy if they can break even in their first year of business.
Companies receive money from selling their products - this money is called the turnover (n- doanh thu, doanh so).
The money that they spend is called the expenditure (n- phi tổn, sự tiêu dung).
They spend money on these things: raw materials (n-vật liệu thô) (= materials in their natural state used to make S.T else, e.g. coal and oil are important raw materials used to make plastics); labour (= employees); overheads (= necessary costs for a company, e.g. rent for building, electricity, telephone)
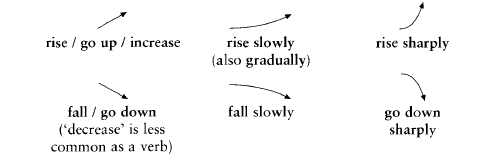
3. Rise and fall
Business people often need to talk about the movement of sales, prices, interest rates, profit and loss, etc. Here are some of the words used to describe these trends (n- phương hướng, xu hướng) (= movements):
Notes: rise, increase, and fall are also used as nouns: a slow rise in interest rates, a steady increase (adj- vững, đều đều) in sales, a sharp fall in profits, a dramatic (=sharp) rise in inflation (n- lạm phát). We can also use be up/down; prices are up by 10%; profits are down by $2m.
4. Businesses and the economy:
In order to grow/expand (= get bigger) and thrive/prosper (v- phát đạt, thịnh vượng) (= do well/ be successful), many companies want or need the following:
_ low inflation, so prices do not go up.
_ low interest rates, so the company can borrow money without paying a lot of interest economic and political stability (= things remain steady (adj- vững, chắc) and stable and there are not sudden (adj) changes in the economic and political situation).
_ a healthy/strong economy (= in good condition), and not an economy in recession (n- tình trạng suy thoái (= in a period of reduced and slow business activity)
_ tax cuts (= tax reductions/lower taxes), so they can keep more of their profit. This often depends on government expenditure, e.g. The government will not be able to reduce taxes if public expenditure continues to rise.
Others:
The continuous increase in the price of things.
Fortunately the company is doing well now.
And it's growing very quickly.
This is one of their main objectives.
Profit have risen considerably.
What is the current inflation rate?
What is the state of the economy at the moment?
Do you think business are optimistic about the future?
Has the government reduced company taxes or personal taxes in the last twelve months?
Has public expenditure risen of fallen int the last twelve months?
Describe the graph as following:
In 1992 sales rose.
In the following year they fell slightly.
In 1995 there was a sharp fall in sales.
In 1996 business improved and there was a steady rise.
And in 1997 sales rose sharply
In the five-year period sales rose by 40,000.
Read More ...